Proper Tree Fertilization: Tips for Healthy Growth and Longevity
Trees are an essential part of our ecosystem, providing us with countless benefits, from purifying the air to providing shelter and food for various species. However, like any living thing, trees need proper care to stay healthy and thrive. One of the most important aspects of tree care is fertilization, which means giving trees the nutrients they need to grow strong and healthy. In this guide, we'll explore why fertilizing trees is so important, the different types of fertilizers you can use, and the best ways to apply them for optimal results.
Why Should You Fertilize Trees?
Just like people, trees need a balanced diet to stay in top shape. The soil where trees grow is their main source of nutrients, but over time, that soil can lose its nutrients due to factors like erosion, nutrient leaching, and rapid tree growth. Fertilizing trees helps replenish these vital nutrients, ensuring they have what they need to grow, develop, and fight off diseases and pests.
When trees are well-fertilized, you’ll notice several benefits:
- Faster growth rates
- Stronger tree structure and shape
- Greater resistance to diseases and pests
- Better ability to handle environmental stress
- Healthier, more vibrant foliage
Types of Fertilizers for Trees
There are various types of fertilizers available, and each has its own set of benefits and drawbacks. Here’s a closer look at the different options:
1. Organic Fertilizers
Organic fertilizers are made from natural materials, such as animal manure, compost, or plant-based substances. These are environmentally friendly and help improve the soil’s overall health by promoting good soil microbes. They release nutrients slowly, which is great for long-term tree health. Some popular organic fertilizers include:
- Compost: Decomposed organic material that enriches the soil.
- Manure: Animal waste that provides essential nutrients.
- Fish Emulsion: A liquid fertilizer made from fish byproducts.
- Bone Meal: A powder made from ground animal bones, rich in phosphorus.
2. Synthetic Fertilizers
Synthetic fertilizers are man-made and consist of chemical compounds that quickly release nutrients into the soil. While they can offer fast results, overuse or incorrect application can harm the soil and environment. Some common synthetic fertilizers are:
- Ammonium Nitrate
- Urea
- Ammonium Sulfate
3. Slow-Release Fertilizers
These fertilizers release nutrients slowly over time, providing a steady supply of essential nutrients throughout the growing season. They’re perfect for trees that need consistent feeding over a longer period. Examples include:
- Osmocote
- Scotts Osmocote
4. Liquid Fertilizers
Liquid fertilizers are applied directly to the soil or leaves, offering a quick and efficient way to deliver nutrients. They’re particularly useful for trees with limited access to soil or when immediate nutrient supplementation is needed. Types include:
- Foliar Sprays
- Soil Injectors
Best Practices for Tree Fertilization
To get the most out of your tree fertilization efforts, it’s crucial to use the right techniques and follow a few essential guidelines:
1. Test the Soil
Before adding any fertilizer, conduct a soil test to find out the pH level and the nutrient content of the soil. This will help you choose the right fertilizer and determine how much to use.
2. Determine the Right Amount
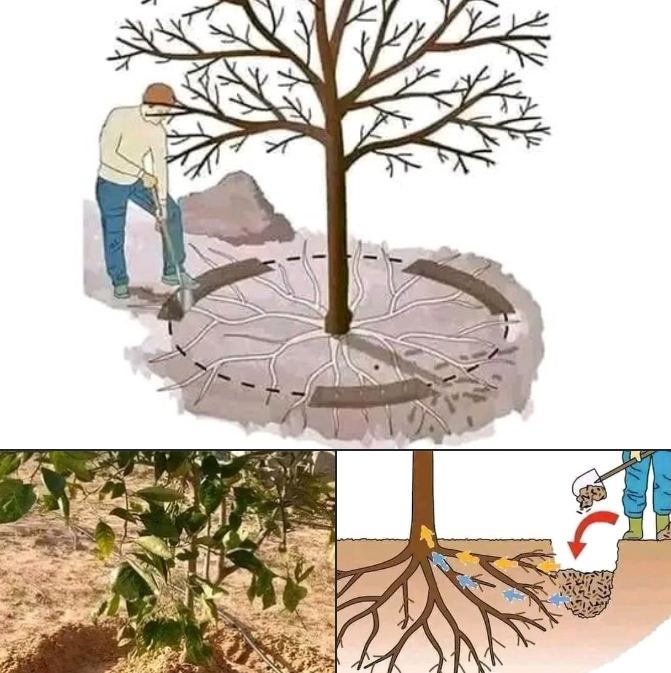
The amount of fertilizer needed depends on the tree’s size, age, and species. A general rule of thumb is to apply 1-2 pounds of fertilizer for every inch of the tree’s diameter, evenly spreading it around the tree’s dripline (the area beneath the outermost branches).
3. Choose the Right Time
When you apply fertilizer is just as important as what you apply. For deciduous trees, fertilize in early spring, just before new growth starts. For evergreen trees, fertilize in late winter or early spring.
4. Apply Fertilizer Correctly
Proper placement is key to avoiding damage to the tree’s roots and promoting healthy growth:
- Broadcast Application: Spread fertilizer evenly around the dripline, being careful to avoid the root flare (where the trunk flares out at the base of the tree).
- Soil Injection: Inject fertilizer directly into the soil, 12-18 inches deep, around the dripline.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While fertilizing your trees is essential, doing it incorrectly can cause more harm than good. Here are some mistakes to avoid:
- Over-Fertilization: Too much fertilizer can lead to soil pollution, water contamination, and damage to the tree.
- Under-Fertilization: Not providing enough nutrients can stunt growth, weaken the tree, and make it more susceptible to diseases and pests.
- Incorrect Timing: Fertilizing at the wrong time can disrupt the tree’s natural growth patterns, leading to poor health and structure.
Conclusion
Fertilizing trees is more than just a routine task; it’s a delicate balance that requires careful consideration and the right approach. By understanding why fertilization is important, choosing the right type of fertilizer, and applying it correctly, you can help your trees grow healthier and stronger. Remember, a well-fertilized tree is not only a beautiful addition to your landscape but also a vital part of a thriving ecosystem. With these tips, you’ll be well on your way to fostering lush, vibrant trees that enhance both your home and the environment.